Glaucoma
Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of blindness in the world. In the United States alone, over 2 million people are diagnosed with the eye disease. While there is no cure for glaucoma, vision loss can be prevented or slowed by early detection, medication, and/or glaucoma surgery.
What is Glaucoma?
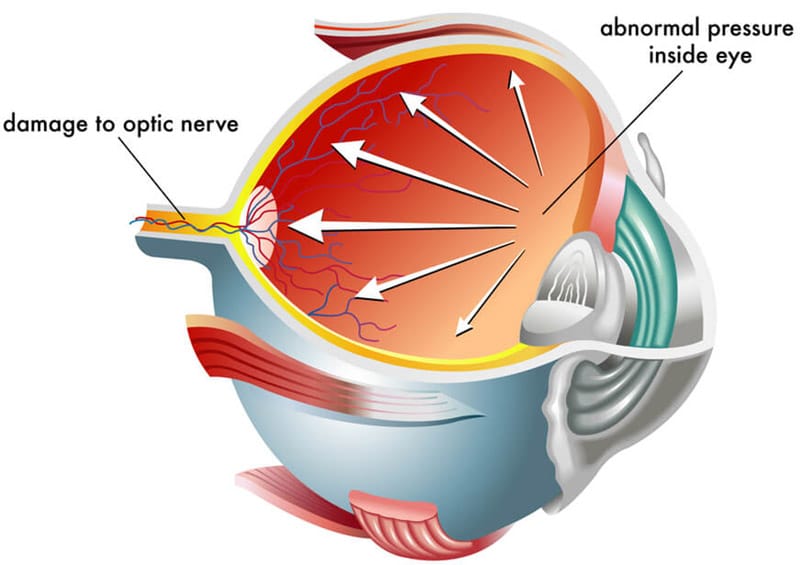
Glaucoma is a blanket term for a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, a bundle of nerves at the back of the eye. The optic nerve transmits visual signals to the brain, which results in the images we see. Optic nerve damage can lead to vision loss and blindness.
What Causes Glaucoma?
The anterior chamber, an area at the front of the eye, is responsible for the passage of clear fluid that flows in and out of the chamber to nourish nearby tissue. In a normal, healthy, eye, the fluid exits the anterior chamber at the open angle of the cornea and iris. Once the fluid reaches this area, it drains out of the eye through the open angle.
In people with open-angle glaucoma, the most common type of glaucoma, the fluid is too slow to drain out of the eye. This results in a buildup of pressure inside the eye, as most of the fluid remains inside. High eye pressure levels put strain on the optic nerve, which can result in vision loss or permanent blindness over time.

What are other types of Glaucoma?
What Are Common Glaucoma Risk Factors?
People who have a family history of glaucoma, diabetics, African Americans over age 40, and Hispanic people over the age of 60 are all at increased risk of developing glaucoma. Thin corneas, chronic eye inflammation, and medications that affect eye pressure levels also increase the likelihood of developing glaucoma.
What Are Common Symptoms of Glaucoma?
Open-angle glaucoma is often referred to as the “silent thief of sight” — there are no noticeable symptoms until significant vision loss has occurred. The disease also develops slowly, so vision loss may not happen for many years. By the time a patient notices changes to their sight, glaucoma has likely advanced to a more serious stage.
Closed-angle glaucoma, also referred to as angle-closure glaucoma or narrow-angle glaucoma, does have symptoms. If you experience any of the following, contact emergency services immediately:
- Severe eye pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Blurry vision
- Excess tearing
What Are Some Common Glaucoma Treatment Options?
Common glaucoma treatment methods include:


